Banking System
- We have Bank Account with 2 Fields – balance and Account Number
- We have Transaction class implementing Runnable
- We create object for account with some initial balance and try to pass as parameter to runnable Transaction Object
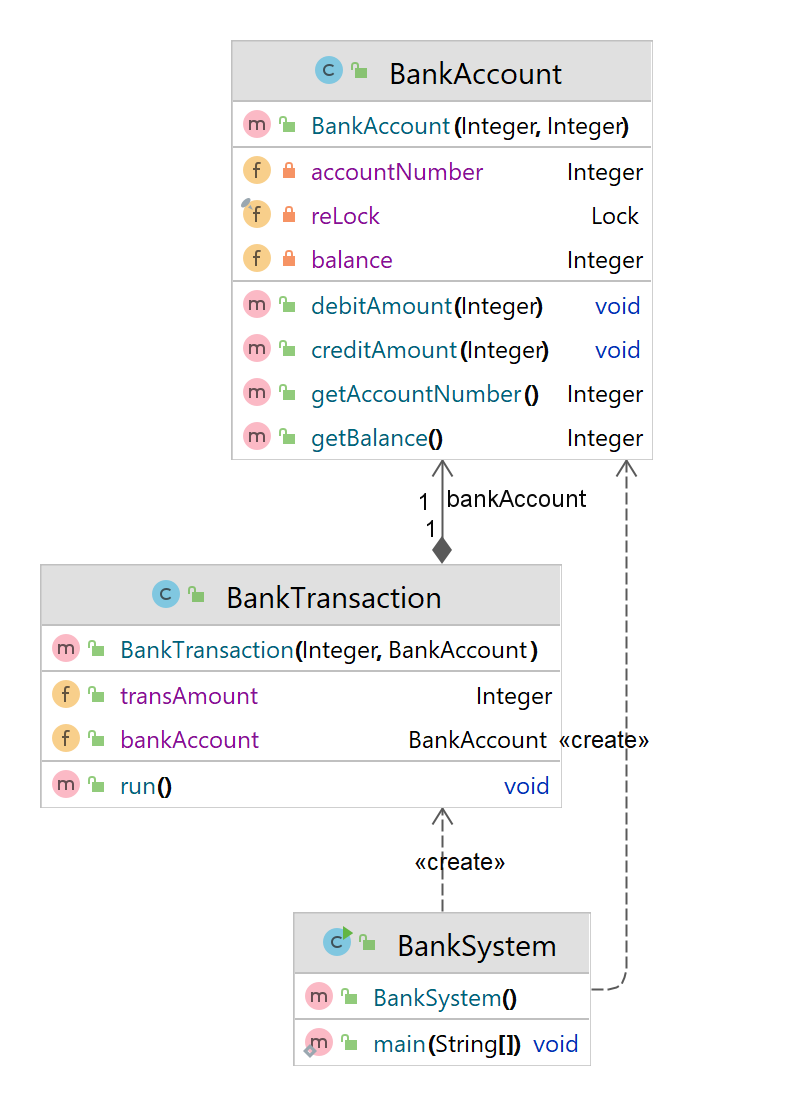
BankAccount.java
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class BankAccount {
private Integer balance;
private Integer accountNumber;
private final Lock reLock = new ReentrantLock();
public BankAccount(Integer balance, Integer accountNumber){
this.balance = balance;
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
}
public void debitAmount(Integer amount){
reLock.lock();
try{
balance -= amount;
}finally {
reLock.unlock();
}
}
public void creditAmount(Integer amount){
reLock.lock();
try{
balance += amount;
}finally {
reLock.unlock();
}
}
public Integer getAccountNumber(){
return this.accountNumber;
}
public Integer getBalance(){
return this.balance;
}
}
BankTransaction.java
public class BankTransaction implements Runnable{
public Integer transAmount;
public BankAccount bankAccount;
public BankTransaction(Integer transAmount, BankAccount bankAccount){
this.transAmount = transAmount;
this.bankAccount = bankAccount;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if(transAmount >= 0){
bankAccount.creditAmount(transAmount);
}else{
bankAccount.debitAmount(Math.abs(transAmount));
}
}
}
BankSystem.java
public class BankSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount objAcc1 = new BankAccount(1000, 101);
BankAccount objAcc2 = new BankAccount(2000, 102);
Thread objThread1 = new Thread(new BankTransaction(50, objAcc1));
Thread objThread2 = new Thread(new BankTransaction(-150, objAcc2));
Thread objThread3 = new Thread(new BankTransaction(250, objAcc2));
Thread objThread4 = new Thread(new BankTransaction(250, objAcc1));
objThread1.start();
objThread2.start();
objThread3.start();
objThread4.start();
try{
objThread1.join();
objThread2.join();
objThread3.join();
objThread4.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
System.out.println("Final Balance in Account " + objAcc1.getAccountNumber() + " with balance " + objAcc1.getBalance());
System.out.println("Final Balance in Account " + objAcc2.getAccountNumber() + " with balance " + objAcc2.getBalance());
}
}
Output
Final Balance in Account 101 with balance 1300 Final Balance in Account 102 with balance 2100