Puzzle 1:Crossing the Bridge Puzzle
Four people need to cross a rickety bridge at night. Unfortunately, they have only one torch and the bridge is too dangerous to cross without one. The bridge is only strong enough to support two people at a time. Not all people take the same time to cross the bridge. Times for each person: 1 min, 2 mins, 7 mins and 10 mins. What is the shortest time needed for all four of them to cross the bridge?
Puzzle 2:Burning Rope Timer:
A man has two ropes of varying thickness (Those two ropes are not identical, they aren’t the same density nor the same length nor the same width). Each rope burns in 60 minutes. He actually wants to measure 45 mins. How can he measure 45 mins using only these two ropes.
He can’t cut the one rope in half because the ropes are non-homogeneous and he can’t be sure how long it will burn.
Puzzle 3:How do you measure 50 Mins in the above scenario?
Puzzle 4:Heaven Gate Puzzle:
You are standing before two doors. One of the path leads to heaven and the other one leads to hell. There are two guardians, one by each door. You know one of them always tells the truth and the other always lies, but you don’t know who is the honest one and who is the liar.You can only ask one question to one of them in order to find the way to heaven. What is the question?
Puzzle 5:King and Wine Bottles
A bad king has a cellar of 1000 bottles of delightful and very expensive wine. A neighboring queen plots to kill the bad king and sends a servant to poison the wine. Fortunately (or say unfortunately) the bad king’s guards catch the servant after he has only poisoned one bottle. Alas, the guards don’t know which bottle but know that the poison is so strong that even if diluted 100,000 times it would still kill the king. Furthermore, it takes one month to have an effect. The bad king decides he will get some of the prisoners in his vast dungeons to drink the wine. Being a clever bad king he knows he needs to murder no more than 10 prisoners – believing he can fob off such a low death rate – and will still be able to drink the rest of the wine (999 bottles) at his anniversary party in 5 weeks time. Explain what is in mind of the king, how will he be able to do so ? (of course he has less then 1000 prisoners in his prisons)
Puzzle 6:Age Puzzles
Salman’s youth lasted one sixth of his life. He grew a beard after one twelfth more. After one seventh more of his life, he married. 5 years later, he and his wife had a son. The son lived exactly one half as long as his father, and salman died four years after his son.How many years did salman live?
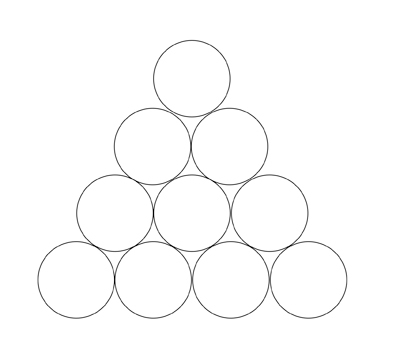
Puzzle 7:Inverted Triangle Puzzle
Triangle is constructed from 10 coins. What is the smallest number of coins that need to be moved to make the triangle point downwards?
Puzzle 8:Birds and Flower Puzzle
Once there came many birds to a pond. There were certain number of lotus flowers in the pond. If each bird occupied one lotus one bird was left alone without any flower. If two birds sat in a flower one flower was left behind. Find the total number of birds and flowers.
Puzzle 9:Time and Machines
If it takes 5 machines 5 minutes to make 5 widgets, how long would it take 100 machines to make 100 widgets?
Puzzle 10:Fastest of 25 Horse
There are 25 horses among which you need to find out the fastest 3 horses. You can conduct race among at most 5 to find out their relative speed. At no point you can find out the actual speed of the horse in a race. Find out how many races are required to get the top 3 horses.
Puzzle 11:A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost?
The Question is tricky in the sense the cost of bat is never unveiled.What is said is how much the bat would cost in excess with respect to ball price.If you are witty you end up telling ball cost is 0.10 which is wrong for below reason.
Puzzle 12: Find age of Daughters
Rishi has three daughters. His friend Shyam wants to know the ages of his daughters. Rishi gives him the first hint.
1.The product of their ages is 36.Shyam says this is not enough information so rishi gives him a second hint.
2.The sum of their ages is equal to my house number. Shyam goes out and look at the house number but still could not figure out ages of daughter
rishi tells Shyam cannot guess and gives him the third hint. 3.The oldest of the girls likes ice-cream.
Puzzle 13: There are 10 robbers who has stolen some coins from a bank and they decided to divide these coins equally among themselves. So they divide the coins into 10 parts but the last robber got 1 coin less than other robbers. So the remaining 9 robbers murder las robber. They again decided to divide the coins into 9 parts. But this time again the last robber got 1 less coin than other robbers. So again the remaining 8 robbers murder last and try to divide all coins in between remaining 8 robbers. But again this time last got one less coin than the other. Now, this process goes on until 1 robber left i.e. The only one robber left take all the coins and run away. Now you have to guess the total number of coins.
Puzzle 14: You have 10 Coins in which 5 are heads up and 5 are tails up. You could not find the which coin is head up and tails up by touching. Now you need to make 2 piles with both the piles having same no of coins heads up and tails up.
Solutions
Puzzle 1:Solution
It is 17 mins.1 and 2 go first, then 1 comes back. Then 7 and 10 go and 2 comes back. Then 1 and 2 go again, it makes a total of 17 minutes.
Puzzle 2:Solution
He will burn one of the rope at both the ends and the second rope at one end. After half an hour, the first one burns completely and at this point of time, he will burn the other end of the second rope so now it will take 15 mins more to completely burn. so total time is 30+15 i.e. 45mins.
Step 1: Burn one rope in both the ends and one rope in one end
Rope 1 x------------------------------------------x
Rope 2 x------------------------------------------
After 30 Mins rope 1 would be completely burnt and rope 2 would be left as below
Rope 1 ...................x........................
Rope 2 ...................x------------------------
Step 2: After 30 Mins lid the other end of rope to measure 15 mins
Rope 1 ...................x........................
Rope 2 ...................x-----------------------x
After 45 Mins
Rope 1 ...................x........................
Rope 2 ...........................................x
x Fire
---- Rope
.... Burnt Rope Ash
Puzzle 3:Solution
50mins can be split to 30 Mins1/2 of an hour + 20 Mins1/3 of the hour which is buring one rope from both ends + burning rope in one end and in middle of rope. We already know to measure 30 mins the rope should be lid on both the ends. To measure 20 mins the rope should be lid in 2 places as below. The second spot can be anywhere in the middle of the rope. Since the rope burns non uniformly it doesn’t matter. Now this should be done again and again until the rope burns out. Basically, we are measuring 1/3rd of hour by burning at 2 ends.
Rope 2 x--------x---------------------------------- After nth minute
Rope 2 x--------------x--------- After n+1 minute
Rope 2 x----x After n+2 minute
Puzzle 4:Solution
“If I ask the other guard about which side leads to heaven, what would he answer?”.
Puzzle 5:Solution
Think in terms of binary numbers.
Number the bottles 1 to 1000 and write the number in binary format (10 digit binary).
bottle 1 = 0000000001
bottle 2 = 0000000010
bottle 500 = 0111110100
bottle 1000 = 1111101000
Now take 10 prisoners and number them 1 to 10, now let prisoner 1 take a sip from every bottle that has a 1 in its least significant bit. Let prisoner 10 take a sip from every bottle with a 1 in its most significant bit. etc.
prisoner = 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
bottle 924 = 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
For instance, bottle no. 924 would be sipped by 10,9,8,5,4 and 3. That way if bottle no. 924 was the poisoned one, only those prisoners would die.
After four weeks, line the prisoners up in their bit order and read each living prisoner as a 0 bit and each dead prisoner as a 1 bit. The number that you get is the bottle of wine that was poisoned.1000 is less than 1024 (2^10). If there were 1024 or more bottles of wine it would take more than 10 prisoners.
Puzzle 6:Solution
x/6 + x/12 + x/7 + 5 + x/2 + 4 = x
where x is salman’s age at the time of his death.Therefore, salman lived exactly 84 years.
Puzzle 7:Solution
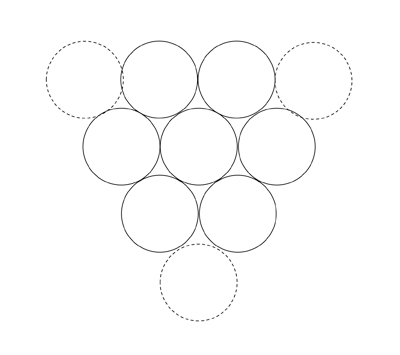
Puzzle 8:Solution
There are 4 lotus flowers and 3 birds. Let the 0s represent the birds. Let the 1s represent the lotus flowers.
CASE 1:Each bird sat on each lotus flower, one bird was left alone.
1 1 1 1
0 0 0
CASE 2:Two birds sat on each lotus flower, one flower was left alone.
(1 1) (1 1)
0 0 0
Another Way of Solving
Let F be the flowers and B be the Birds. If Birds and Flower are equal in Number then F=B. Below the Equations are Derived from Birds Perspective.
As per Case1 B = F+1 (If one bird is sitting in one flower then one more flower is required)
As per Case2 B/2 = F-1 (If 2 birds occupy flower then one flower is extra)
From Case1 F = B/2+1 Replacing the value of F in Case1
B = B/2+1+1
2B=B+4;
B(Birds)=4;
Replacing B=4 in Case1
F(Flowers)=3;
Puzzle 9:Solution
5 Minutes
Puzzle 10:Solution
- Step1:Split the horses into five sets and race among them.At the end of Five race you could identify the fastest horse in the set
- Step2:Now race the top 5 horses from 5 set and get the fastest of all horse.It is 41 in our case
- Step3:Reorder the set in such a way that Fastest horse set comes first ending up with slowest horse.
- Step4:Now we can remove the remaining horses from last 2 groups as we know for sure that horses in those group cannot be second and third fastest horse since there are horses faster than the horses in 4 and 5th from the 6th race we conducted
- Step5:Now I could remove the remaining horses in third set since I know they could not be 3rd fastest as we know the fastest horse in group
- Step6:Lets remove the other 3 horses in second group as I know 3rd fastest horse is in third group(Race2)
- Step7:I am going to eliminate the last 2 horses in first group(Race3) since we are interested in first 3 fastest horse
- Step8: Lets have a final race 7 to find the fastest three horse from set of {24,21,26,36,20,30} which is {36,30}
Step1
Race1 10 36 11 20 15
Race2 15 18 19 10 30
Race3 21 24 10 41 10
Race4 11 10 19 4 13
Race5 25 17 6 9 19
Race1 36 20 15 11 10
Race2 30 19 18 15 10
Race3 41 24 21 10 10
Race4 19 13 11 10 4
Race5 25 19 17 9 6
Step2 and Step3
Race3 41 24 21 10 10
Race1 36 20 15 11 10
Race2 30 19 18 15 10
Race5 25 19 17 9 6
Race4 19 13 11 10 4
Step4
Race3 41 24 21 10 10
Race1 36 20 15 11 10
Race2 30 19 18 15 10
Step5
Race3 41 24 21 10 10
Race1 36 20 15 11 10
Race2 30
Step6
Race3 41 24 21 10 10
Race1 36 20
Race2 30
Step7
Race3 41 24 21
Race1 36 20
Race2 30
Step8
Race3 41
Race1 36
Race2 30
Fastest Horse 1 41
Fastest Horse 2 36
Fastest Horse 3 30
Refer here
Puzzle 11:Solution
x = ball
y = bat
x + y = 1.10;
y = x + 1;
x + x + 1 = 1.10;
2x + 1 =1.10;
2x = 0.10;
x=0.5;
Cost of ball = 0.5;
Cost of bat = 1.05;
Puzzle 12:Solution
Shyam is able to guess after the third hint. Can you guess what are the ages of three daughters?
Hint 1: The product of their ages is 36
1 × 1 × 36 = 36
1 × 2 × 18 = 36
1 × 3 × 12 = 36
1 × 4 × 9 = 36
1 × 6 × 6 = 36
2 × 2 × 9 = 36
2 × 3 × 6 = 36
3 × 3 × 4 = 36
Hint 2: The sum of their ages is equal to my house number
1 + 1 + 36 = 38
1 + 2 + 18 = 21
1 + 3 + 12 = 16
1 + 4 + 9 = 14
1 + 6 + 6 = 13
2 + 2 + 9 = 13
2 + 3 + 6 = 11
3 + 3 + 4 = 10
Here in is the crux of the puzzle, we obviously don’t know the man’s door number. We can assume that the second man does. At this stage we are only assuming, but the fact that he is able later, to definitively answer the puzzle will mean that this is no longer an assumption. And remember we are trying to explain what happened. Even with the door number, the second man does not know the ages of the daughters, so it must still be ambiguous, there are only two combinations that have the same total which leads to ambiguity.
1 + 6 + 6 = 13
2 + 2 + 9 = 13
Hint 3:The oldest of the girls likes ice-cream
Since there is only one oldest the combination is 2 + 2 + 9 = 13.The daughters age is 2,2,9.
If the above question is asked with third hint youngest daughter has blue eyes then the answer would be 1 + 6 + 6 = 13.The daughters age is 1,6,6
Puzzle 13:Solution
Let the robbers be
Robber1,Robber2,Robber3,Robber4,Robber5,Robber6,Robber7,Robber8,Robber9,Robber10
After Split1
Robber1,Robber2,Robber3,Robber4,Robber5,Robber6,Robber7,Robber8,Robber9
After Split2
Robber1,Robber2,Robber3,Robber4,Robber5,Robber6,Robber7,Robber8
After Split3
Robber1,Robber2,Robber3,Robber4,Robber5,Robber6,Robber7
.
.
After Split10
Robber1
Let the total coins be N.After the first split Robber10 gets 1 coin less than remaining so they kill Robber10. So in order for equal split it should be (N+1) Coins in total.The same thing happens again and again. Let’s substitute robbers with numbers for ease of split.
Robber1 - 1
Robber2 - 2
Robber3 - 3
Robber4 - 4
Robber5 - 5
Robber6 - 6
Robber7 - 7
Robber8 - 8
Robber9 - 9
Robber10 - 10
If the coins needs to be equally split, we need to arrive at a number which is divisible by all the robbers. We need to find Least Common Multiple for above number
Total Coins for equal split = LCM(10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1) = 2520
Since we have one coin less that LCM of above number the total coins robbers took is 2519.
Puzzle 14:Solution
Make 2 piles with the equal number of coins. Now, flip all the coins in one of the pile.
Case 1:
P1 : H T T T T
P2 : H H H H T
After flipping
P1 : T H H H H
P2 : H H H H T
P1(heads) = P2(heads)
Case 1:
P1 : H T H T T
P2 : H H T H T
After flipping
P1 : T H T H H
P2 : H H H H T
P1(heads) = P2(heads)