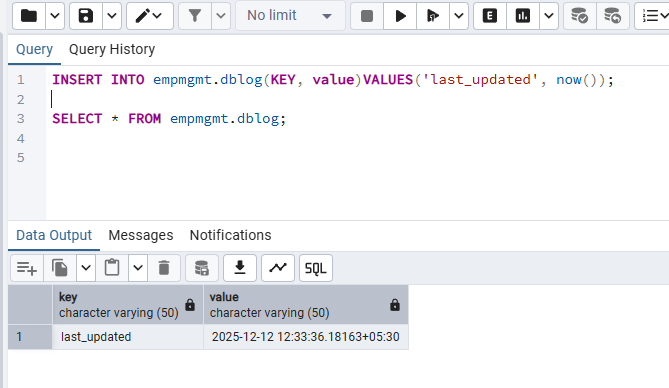
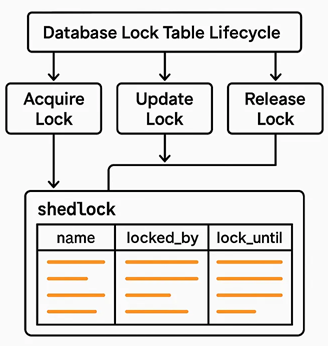
Shedlock prevents concurrent execution of scheduled tasks in distributed systems. In a server where multiple instance of same JAR running, shedlock prevents simultaneous execution of task by different instance at the same time. By this shedlock prevents race conditions and prevents multiple nodes from executing the same task simultaneously, which can lead to data corruption or duplication
Before Shedlock
Application Schedule Job
└─▶ PCF Inst A: tries to gets lock → runs job
└─▶ PCF Inst B: tries to gets lock → runs job
└─▶ PCF Inst C: tries to gets lock → runs job
Post Shedlock
Application Schedule Job
└─▶ PCF Inst A: tries to gets lock → runs job
└─▶ PCF Inst B: Waits for lock release → runs job
└─▶ PCF Inst C: Waits for lock release → runs job
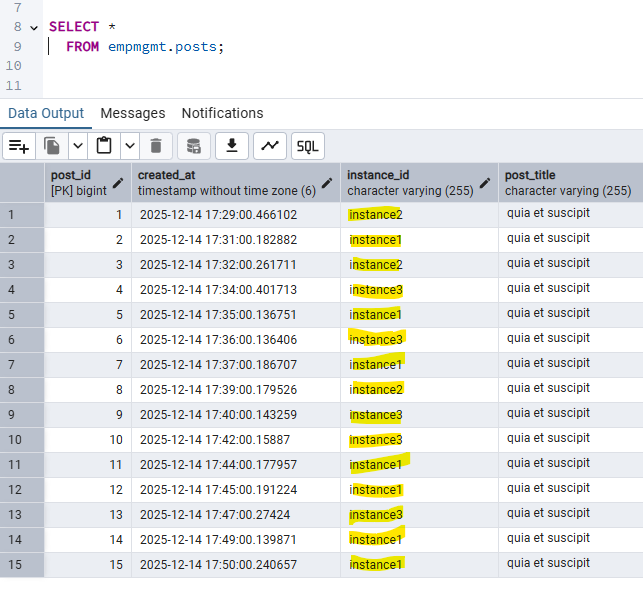
If you have same scheduled job running in more than one instance.
- When a scheduled task is triggered, ShedLock checks a shared lock (e.g., in a database table).
- If the lock is free, it acquires it and runs the task.
- If another instance already holds the lock, the task is skipped.
- The lock has an expiration time to handle crashes or failures gracefully.
Sending emails or notifications, Generating reports, Cleaning up expired sessions or data, Syncing data with external systems
FAQ
atLeast and atMost Lock time in shedlock?
In ShedLock, atLeast and atMost are parameters used to control the duration of the lock for scheduled tasks. They help ensure that tasks are executed safely and efficiently in distributed environments.
Example:
atLeast = 5m means the lock will stay held for at least 5 minutes, even if the task finishes in 1 minute. this prevents other instances from immediately picking up the task again, useful for throttling or spacing out executions.
atMost = 10m means the lock will automatically release after 10 minutes, even if the task hasn’t finished. atMost is needed incase the task fails and to prevent resource from holding for long time.
The @SchedulerLock annotation in ShedLock is used to control distributed locking for scheduled tasks
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 * * * *") // every hour
@SchedulerLock(name = "hourlyTask", atLeast = "30m", atMost = "1h")
public void hourlyTask() {
// task logic here
}
- The task runs only once per hour across all instances.
- The lock is held for at least 30 minutes, even if the task finishes early.
- The lock is released after 1 hour, even if the task hangs.
Can another instance Instance2 can execute the job, if Instance1 job is completed within 30 Minutes(atleast Time)?
No. The atLeast duration is a guaranteed lock time, not tied to actual job execution. Instance2 cannot start the job during this 30-minute window because the lock is still active. Even when the instance1 job is completed within 30 minutes instance2 job cannot be started unless the lock is released.
What happens when atLeastTime is more than Schedule Interval of Job
Lets say we have a job which runs every 4 minutes. We have a Shedlock which has minimum lock time of 5 Minutes and max of 10 Minutes. Now in this scenario job would run in 8th, 16th, 28th, 36th Minute the job would run
|-------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|-------------|
TimeLine 0-------------5-------------10------------15------------20------------25------------30------------35
Lock Time <------L----->|<-----NL---->|<-----L----->|<-----NL---->|<-----L----->|<-----NL---->|<-----L----->|
Job Exe Inter 0----------4----------8----------12----------16---------20---------24---------28---------32--------
L -> Resource Locked
NL -> Resource Unavailable
In the above Job Execution would work when the Lock Time is NL
What if there is a Negative Scenario as below
- Where the resource is locked and shedlock releases the resource
- The Time of Release of Resource and Job Execution Interval are same
Lets have a scenario where the atmost Time is 5 Minutes and Job Execution Interval is also 5 Minutes. In this case the Job may or may not run as expected.
The Job runs at 00:05:00 When Lock is released on 00:05:00
The Job wont run at 00:05:00 When Lock is released on 00:05:01
Its a good practice to have atmost time less than schedule interval time. I.E. 00:04:50 in the above case
Should I use Shedlock while updating db tables?
If updating database tables as part of a scheduled task in a distributed system using shedlock would be good option. this prevents Duplicate Execution and Data Integrity
Why we are defining lock timing at 2 places?
@EnableSchedulerLock(defaultLockAtMostFor = "PT4M")
vs
@SchedulerLock(name = "fetchPosts", lockAtMostFor = "PT2M", lockAtLeastFor = "PT1M")
@EnableSchedulerLock sets defaults for all tasks. A fallback setting for all tasks.
@SchedulerLock gives per-task overrides with more precise control. Fine-grained control, overriding the default for specific jobs.
What is Race Condition?
# Initial balance = 100
Thread A: balance += 50 # Expected: 150
Thread B: balance -= 30 # Expected: 70
If both threads read the balance at the same time (100), and then write their results, the final balance could be either 120, 150, or 70, depending on timing