
Author Archives: admin
Oracle Sorting Alphanumeric Values
While Doing sort in oracle the Normal sort works differently for the following Data
CREATE TABLE TestTable(Col1 VARCHAR2(20));
insert into TestTable values('A11');
insert into TestTable values('A260');
insert into TestTable values('A10');
insert into TestTable values('A5');
A11 A260 A10 A5
SELECT *
FROM TestTable
ORDER BY col1;
Output
A10 A11 A260 A5
You may expected A5 before A10 and A11. But It would have been before A10 and A11 when it is A05. The workaround for this is as below.
SELECT * FROM TestTable ORDER BY lpad(col1,9999999);
Output
A5 A10 A11 A260
How to add Cumulative Total Oracle Query
SELECT * FROM EMP;
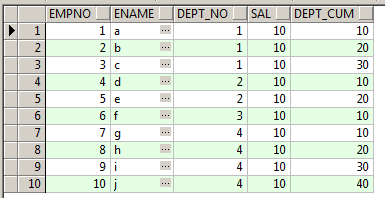
SELECT EMPNO
,ENAME
,dept_no
,SAL
,SUM(sal) over(ORDER BY empno) AS dept_cum
FROM EMP
ORDER BY empno;
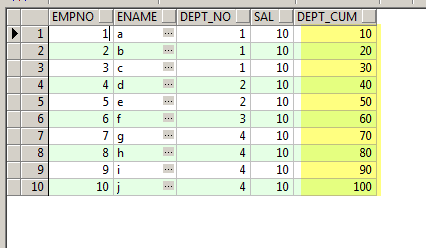
Lets group the Cumulative Sum Based on DepartmentId
SELECT EMPNO
,ENAME
,dept_no
,SAL
,SUM(sal) over(PARTITION BY dept_no ORDER BY empno) AS dept_cum
FROM EMP
ORDER BY empno;

Hinduism Philosophy Notes
Session 1
As per the Hindu Scriptures Happiness is Realization. Realization of Self.It can also be said as pursuit of realization of things.
The difference between effectiveness and efficiency can be summed up shortly, sweetly and succinctly – Being effective is about doing the right things, while being efficient is about doing things right.
Karma
The Word karma means Action (or) Result of Action
As per the Yoga Sutras karmas of the past, present, and future are called Sanchitta, Parabda, and Agami.
Sanchitta(Karma which you have already Collected) – .This is accumulated past actions or karmas waiting to come to fruition. Sanchitta is the storehouse of every action you have ever done, in all the lifetimes you have ever lived. These are all of the unresolved past actions waiting to reach resolution.
Parabda(Karma in Present Life) – what you are doing now, in this lifetime and its result.
Agami(Karma you have collected in Present Life for Future) – Future actions that result from your present actions are called agami karma. As you attempt to resolve past karma, you unavoidably create new karmas that you may or may not be able to resolve in your present life. If you don’t resolve them now, they will go into the storehouse to be resolved in a future life.
To put in simple words
Sanchitta – is like Fixed Deposit.The amount you have invested is there until maturity.
Parabda – is like Current Account where you would be drawing interest now and then.
Agami – is like Recurring Deposit, What ever amount you have added will add more taking it to consideration.You are trying to dissolve karma.But you are forced to add more into your account due to actions which you carry out to dissolve karma.
saṃskāra – (impression, impact, imprint)– The word samskara comes from the Sanskrit sam (complete or joined together) and kara (action, cause, or doing). In Tamil its called vinnai.Its just like a seed which is waiting to get sprouted. Every action we do in our life is like a seed.The time it sprouts and yield the fruit is different based on types of actions we did.
As far as we are part of the system we do actions and we all have left samskara(Vinnai). The whole goal is to get rid of karma to avoid further samskara.with the help of god we are going to get rid of karma.
Samskara is like taking loan with the intention of paying another Loan. But EOD you will still be a borrower to some one else.To get rid of this cycle we are taking gods help instead of borrowing from some one else.
In patanjali yoga we surrender to god and try to get rid of karma.
Vedic texts mention that human body is only the physical abode of soul. The soul is considered to be enveloped in five sheaths which we call as Pancha kosha.Soul (atman) is wrapped inside five layers (Pancha kosha).
annamaya kosha – anna means “food” or “physical matter.” maya means “made of” andThis is the life energy that governs your biological processes, from breathing to digestion to the circulation of your blood.
pranamaya kosha – prana means “air” – Exercises like diaphragmatic breathing, the complete yogic breath, and alternate nostril breathing are specifically designed to enhance the proper functioning of your second sheath.
manomaya kosha – mano means “body made of thought processes” – Mind as distinctly different from intelligence
The pranamaya kohsa operates from the moment of our first breath to our last, but the manomaya kosha shuts down temporarily on a daily basis, regenerating itself during the state of deep sleep.
vijnanamaya kosha – vijnana means “the power of judgment or discernment” – It’s often translated as “intellect,” but the real meaning is broader, encompassing all the functions of the higher mind, including conscience and will. ability to discern between right and wrong.
anandamaya kosha – ananda means “Bliss” – the final and thinnest veil standing between our ordinary awareness and our higher Self. Many individuals who’ve had near-death experiences have reported experiencing a brilliant white light radiating all-embracing wisdom and unconditional love.
Actually it is seven koshas if we go in more details of vedic texts
For Further learning on Koshas refer the link
Ahamkara
Aham – I
Kara – Exists
Every Organism in this world has Ahamkara. Ahamkara is mistaken with the word Ego.I alone Exist is Ego.Even Ant has Ahamkara. When you place your finger on the line the Ant moves it bites you.
Session 2
Vairagya – Vairagya is the ability to sustain dispassion towards things.It should be reinforced again and again.Its just like motivation which gives the initial thrust.At a point of time every one of us gets vairagya.But how long it lasts makes the difference.
Vairagya is total absence. Absence in first place. Monkey Fasting Story. Gnana leads to vairagya.
Vairagya can be maintained by again and again listening to good things.Its like Knowledge and Vairagya cycle as shown in image below.
Brahmacharyam – One who is devoted to study of vedhas
Yama and Nachiketa
Nachiketa asked yama why some people do good and bad things in life.For that yama replied its not Good and Bad which matters its pleasant and unpleasant matters.
The mind always chooses Pleasant irrespective of Good and Bad.
Again nachiketas asked why is it so.Yama replied its because of nature of manas.
Mind is a Beast
Once upon a time there lived demon inside jar.The demon had enormous power to get done with any task given but it needs a master to guide it.The demon is slave for its master until it runs out of job. Once it ceases to work or if master stops giving work it will make the Master as Slave.
One day a guy released the demon from this Jar and started giving tasks.Since the demon is so powerful it finished all the task given to it within few minutes. At one point of time the master is running out of tasks.
Now the Demon became the Master and the person who freed the demon should become slave.The person started running in forest to prevent getting slaved and met a Buddha.He asked him for help.After hearing the story the Buddha asked to draw a line on wall and to make the demon to start going up and down in the line.By doing this the demon is always engaged indefinitely.
The Demon in the above context is our Mind.It is very powerful and processes huge volume of things in fraction of seconds.Once our mind is Idle this Body will become slave to It. By attaining sammadhi we try to tie our mind in some thing and prevent this body from getting enslaved.
Karma – Freewill vs Determinism
Freewill – I can do anything I want
Determinism – I can do anything with gods will
This moment is Determinism(inevitable) but the next moment is free will.
Until you get gnana everything will be path of karma/i.e you met with accident you can shout at the person(determinism) or you can act better by freewill.
In vedanta Samadhi means union with God but in yogasutra samadhi means union with something(or) inner soul.
Meaning of bhagavadgita Picture
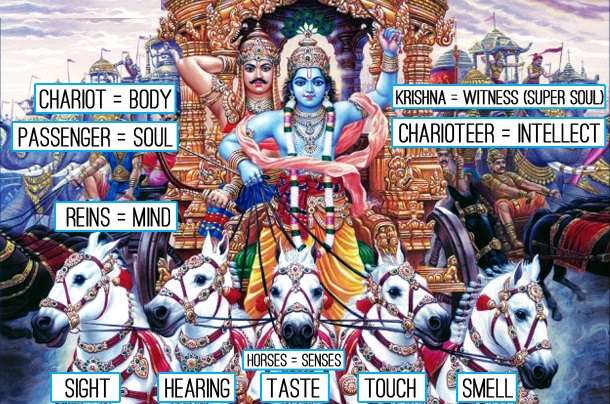
As far Many have Known Bhagavadgita is all about conversation between Krishna and Arjuna.Here is the perspective which you haven’t seen before
- Arjuna is the Soul, our Consciousness which is in our physical body
- Chariot is our physical body
- 5 Horses are the 5 Senses (tongue, eyes, ears, nose and skin)
- The reins, symbolize the mind
- Krishna is the Intellect, Buddhi which guides the senses(Horses)
In short through buddhi we should control our mind and senses and move towards the Ultimate Consciousness.
Difference between Mind and Buddhi
Mind is the one which provides you with options. Buddhi is the one which allows you to select the Right Option.
Empty Check in Oracle
SELECT 'Equal' FROM DUAL WHERE NVL(NULL,'') = '';
Output
SELECT 'Equal' FROM DUAL WHERE NVL(NULL,'~') = '~';
Output
Empty
While Passing Parameters to Procedure its should be
SELECT 'Equal' FROM DUAL WHERE NVL(col_name, '~') = NVL(p_param, NVL(col_name, '~'));
Sorting with Date in Oracle Select
While sorting with date it should be converted using to_date first with the required format.
Other wise while sorting in Desc Order 31-02-2015 will come in front of 21-10-2015
SELECT * FROM tableName ORDER BY to_date(DATE_OF_BIRTH, 'DD-MM-YYYY');
Custom Attribute in HTML Tag
<a data-pagenum="2" onclick="paginate(this)" href="#">2</a>
var pageNum = $(pThis).data("pagenum");
//Outputs 2 in Console
console.log(pageNum);
Oracle Using Limit with ROWNUM
In Oracle if you want to limit the records based on ROWNUM(mostly while doing pagination) the between is not going to work.
Below Doesn’t work
SELECT Column1, Column2, ......., Column N FROM TableName WHERE ROWNUM Between 5 AND 10;
The alternate for this is as Follows
SELECT * FROM
(SELECT rows_to_page.*, ROWNUM rnum FROM
(SELECT Column1, Column2, ......., Column N
FROM TableName
WHERE ROWNUM Between 5 AND 10) rows_to_page
WHERE ROWNUM < end_offset)
WHERE rnum > start_offset;
Working with Date in Oracle
--16-12-2015 12:33:21 SELECT SYSDATE FROM dual; --16-12-2015 SELECT trunc(SYSDATE) FROM dual; --16-12-2015 SELECT to_date(SYSDATE) AS ToDate FROM dual; --16-12-2015 SELECT to_date(SYSDATE, 'DD-MM-YY') AS ToDate FROM dual; --16-12-2015 SELECT to_char(SYSDATE, 'DD-MM-YYYY') AS ToDate FROM dual;