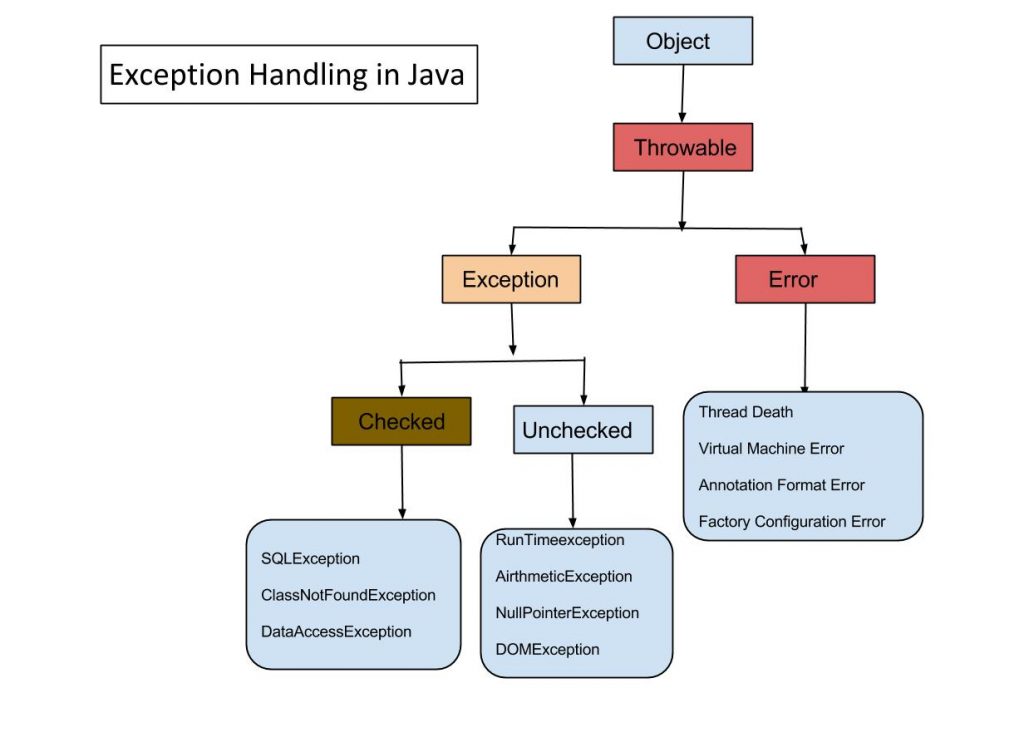
Q1.Explain Exception Hierachy?
Q2.What are important methods of Java Exception Class?
String getMessage() – This method returns the message String of Throwable and the message can be provided while creating the exception by it’s constructor.
String getLocalizedMessage() – This method is provided so that subclasses can override it to provide locale-specific message to the calling program. Throwable class implementation of this method simply uses getMessage() method to return the exception message.
synchronized Throwable getCause() – This method returns the cause of the exception or null id the cause is unknown.
void printStackTrace() – This method prints the stack trace information to the standard error stream, this method is overloaded and we can pass PrintStream or PrintWriter as an argument to write the stack trace information to the file or stream.
Q3.What is multi-catch block?(or) How can I catch multiple Java exceptions in the same catch clause?
We can catch multiple exceptions in a single catch block. catching all the exceptions in a single try block, you will notice that catch block code looks very ugly and mostly consists of redundant code to log the error, keeping this in mind Java 7 one of the features was multi-catch block.
catch(IOException | SQLException | Exception ex){
logger.error(ex);
throw new MyException(ex.getMessage());
}
Q4.What is try-with-resources does?
try-with-resources was introduced because some resources used in Java (like SQL connections or streams) being difficult to be handled properly; as an example, in java 6 to handle a InputStream properly you had to do something like
InputStream stream = new MyInputStream(...);
try {
// ... use stream
} catch(IOException e) {
// handle exception
} finally {
try {
if(stream != null) {
stream.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
// handle yet another possible exception
}
}
Using try-with-resources we can do the same thing as below and close() is automatically called, if it throws an IOException, it will be supressed
try (InputStream stream = new MyInputStream(...)){
// ... use stream
} catch(IOException e) {
// handle exception
}
Any object that implements java.lang.AutoCloseable, which includes all objects which implement java.io.Closeable, can be used as a resource.
Q5.Advantages of try-with-resources does?
- Readable code and easy to write and Number of lines of code is reduced as no need for finally block
- We can open multiple resources in try-with-resources statement separated by a semicolon. For example, we can write following code.
- When multiple resources are opened in try-with-resources, it closes them in the reverse order to avoid any dependency issue. You can extend my resource program to prove that.
- Automatic resource management.
Q6.What is Exception Masking?
When code in a try block throws an exception, and the close method in the finally also throws an exception, the exception thrown by the try block gets lost and the exception thrown in the finally gets propagated. This is usually unfortunate, since the exception thrown on close is something unhelpful while the useful exception is the informative one. Using try-with-resources to close your resources will prevent from exception-masking from taking place.With try-with-resources, if the try block throws an exception and the close method also throws an exception, then the exception from the close block gets tacked on to the original exception. the exception from the finally block is added to the list of exceptions suppressed by the exception from the try block. As an exception unwinds the stack, it can accumulate multiple suppressed exceptions.On the other hand if your code completes normally but the resource you’re using throws an exception on close, that exception (which would get suppressed if the code in the try block threw anything) gets thrown.
Q7.How Autocloseable works?
A try-with-resources statement makes sure that all declared resources will be closed at the end of the statement.To close a resource its should implement the AutoCloseable interface Object of classes that implements autoCloseable are considered for deallocation in try-with-resources.JVM will call close() automatically for you
public class MyResource implements AutoCloseable
{
public void close() throws Exception
{
System.out.println("Closing!");
}
}
try(MyResource res = new MyResource())
{
//use res here
}
Q8.Difference between Closeble and Autocloseable works?
Closeable.close() throws IOException. A lot of close() methods that could benefit of try-with-resources throw other checked exceptions (eg java.sql.Connection.close() so AutoCloseable.close() throws Exception. Changing the existing Closeable contract would break all existing applications/library relying on the contract that close() only throws IOException and not all (checked) exceptions.
Q9.How to get Suppressed Exceptions?
java 7 functionality has been provided to retrieve suppressed Exceptions. You can call public final java.lang.Throwable[] getSuppressed() function on the catched throwable object to view the suppressed Exceptions.
public final void addSuppressed(Throwable exception)
Appends the specified exception to the exceptions that were suppressed in order to deliver this exception.
public final Throwable[] getSuppressed()
Returns an array containing all of the exceptions that were suppressed, typically by the try-with-resources statement, in order to deliver this exception.
public static T suppress(final T t, final Throwable suppressed)
public static Throwable [] getSuppressed(final Throwable t) {
addSuppressed Example
public static void memberFunction() throws Exception
{
Throwable th = null;
DirtyResource resource= new DirtyResource();
try
{
resource.accessResource();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
th = e;
}
finally
{
try
{
resource.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
if(th != null)
{
e.addSuppressed(th); //Add to primary exception
throw e;
}
}
}
}
getSuppressed Example
public static void main(String[] arguments) throws Exception
{
try
{
memberFunction();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
err.println("Exception encountered: " + ex.toString());
final Throwable[] suppressedExceptions = ex.getSuppressed();
final int numSuppressed = suppressedExceptions.length;
if (numSuppressed > 0)
{
err.println("tThere are " + numSuppressed + " suppressed exceptions:");
for (final Throwable exception : suppressedExceptions)
{
err.println("tt" + exception.toString());
}
}
}
}
Errors vs Exception
Errors should not be caught or handled.An Error is a subclass of Throwable that indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. Most such errors are abnormal conditions.
i.e AnnotationFormatError, AssertionError, LinkageError, VirtualMachineError
Example: OutOfMemoryError – Not much you can do as your program can no longer run.
Exceptions are often recoverable and even when not, they generally just mean an attempted operation failed, but your program can still carry on.
Example: IllegalArgumentException – Passed invalid data to a method so that method call failed, but it does not affect future operations.
What is difference between Checked Exception and Unchecked Exception?
Checked Exception
The classes that extend Throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as checked exceptions e.g.IOException,SQLException etc. Checked exceptions are checked at compile-time.
Unchecked Exception
The classes that extend RuntimeException are known as unchecked exceptions e.g. ArithmeticException,NullPointerException etc. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time.
Is it necessary that each try block must be followed by a catch block?
It is not necessary that each try block must be followed by a catch block. It should be followed by either a catch block OR a finally block. And whatever exceptions are likely to be thrown should be declared in the throws clause of the method.
Can finally block be used without catch?
Yes, by try block. finally must be followed by either try or catch
Is there any case when finally will not be executed?
finally block will not be executed if program exits(either by calling System.exit() or by causing a fatal error that causes the process to abort).
Can subclass overriding method declare an exception if parent class method doesn’t throw an exception ?
Yes but only unchecked exception not checked.
What is exception propagation ?
Forwarding the exception object to the invoking method is known as exception propagation. By default Unchecked Exceptions are forwarded in calling chain (propagated).
Method1() //Exception Occured
Method2()
Method3()
main()
In the above example exception occurs in Method1() method where it is not handled,so it is propagated to previous Method2() method where it is not handled, again it is propagated to Method3() before main method where exception is handled.
