Multiprocessing is more than one process in execution where as Multithreading is executing multiple threads within same process. One of the main requirement of MultiProcessing is Multi Core Processor.
Multiprocessing: In a cinema, multiple movies are screened simultaneously in different theaters. Each screening represents a separate process. For instance, one theater might be showing an action movie, another might be showing a romantic comedy, and a third might be screening a documentary. Each screening operates independently, with its own audience and projection equipment.
Multithreading: Within a single screening, there are different tasks being performed concurrently to ensure a smooth movie-watching experience. For example, while the movie is playing, the cinema staff might be selling tickets at the box office, preparing popcorn at the concession stand, and monitoring the theater for any disturbances. These tasks can be seen as threads within the same process (screening). They share resources such as the cinema lobby, staff members, and facilities.
A context switch (also sometimes referred to as a process switch or a task switch) is the switching of the CPU (central processing unit) from one process or thread to another.
Irrespective of Single or Multi Core Context Switching happens.
- suspending the progression of one process and storing the CPU’s state (i.e., the context) for that process somewhere in memory
- Retrieving the context of the next process from memory and restoring it in the CPU’s registers
- Returning to the location indicated by the program counter (i.e., returning to the line of code at which the process was interrupted) in order to resume the process.
No. If that happens, It would be resource consuming and no task gets Completed.If that happens less, You see process hanging. Context Switching should be always decided by Operating system by taking no of threads.
You and your friend has visited restaurant and seated in a table.
You(Processor) have been tasked to Eat and Sing at same Time. If you take a bite – Stop Eating – Start Singing – Sing few lines – Stop Singing – Resume Eating this is concurrency in action
You(Processor1) and Your Friend(Processor2) have been tasked to Eat and Sing where one person sings and another eats at same time. This is Parallelism.
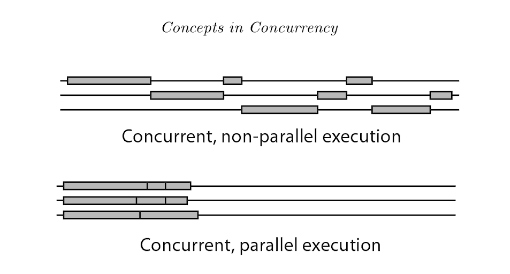
Concurrency is when two or more tasks can start, run, and complete in overlapping time periods. It doesn’t necessarily mean they’ll ever both be running at the same instant. context switching is a key part of enabling concurrency in a single-core system For example, multitasking on a single-core machine.In Concurrency Interruptability exists
Parallelism is when tasks literally run at the same time, e.g., on a multicore processor.In Parallelism Independabality exists.
Concurrency Concurrency + parallelism
(Single-Core CPU) (Multi-Core CPU)
___ ___ ___
|th1| |th1|th2|
| | | |___|
|___|___ | |___
|th2| |___|th2|
___|___| ___|___|
|th1| |th1|
|___|___ | |___
|th2| | |th2|
In both cases we have concurrency from the mere fact that we have more than one thread running.If we ran this program on a computer with a single CPU core, the OS would be switching between the two threads, allowing one thread to run at a time.If we ran this program on a computer with a multi-core CPU then we would be able to run the two threads in parallel – side by side at the exact same time.
Concurrency is about dealing with lots of things at once. Parallelism is about doing lots of things at once.
Scenario 1:
Completed Progressing
Timeline <----------------------->|<-------------------------------->
P1 |-----------|--------|------------|------|-----------------|
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
Scenario 2:
Completed Progressing
Timeline <---------------->|<----------------------------------------->
P1 |--------|--------|---------|-----|--------|--------|--------|
T1 T2 T3 T1 T3 T4 T5
Scenario 3:
Completed Progressing
Timeline <-------------------------------------->|<------------------->
P1 |--------|--------|---------|-----|--------|--------|--------|
T1 T2 T3 T1 T6 T4 T2
P2 |--------|--------|---------|-----|--------|--------|--------|
T2 T1 T1 T2 T3 T6 T3
Scenario 4:
Completed Progressing
Timeline <-------------------------------------->|<------------------->
P1 |--------|--------|---------|-----|--------|--------|--------|
T1 T2 T3 T1 T6 T2 T2
P2 |--------|--------|---------|-----|--------|--------|--------|
T4 T5 T4 T7 T5 T4 T8
Scenario 1:
Completed Thread: T1, T2 (2)
Progressing Thread: T3 (1)
Neither Concurrent Nor Parallel – Sequential Execution
Scenario 2:
Completed Thread: T2 (1)
Progressing Thread: T1,T3 (>2)
Concurrent Not Parallel
Scenario 3:
Completed Thread: T1,T2 (2)
Progressing Thread: T3,T4,T6 (>3)
Concurrent and Parallel Execution
Scenario 4:
Completed Thread P1: T1,T3
Progressing Thread P1: T2,T6
Completed Thread P2: T8
Progressing Thread P2: T4,T5
In the above keeping the status of the completed and progressing threads aside, being Multi Core processor the threads are not shared
among the processor. This is example of
Parallel Not concurrent
- An application can be concurrent but not parallel, which means that it processes more than one task at the same time, but no two tasks are executing at the same time instant.
- An application can be parallel — but not concurrent, which means that it processes multiple sub-tasks of a task in multi-core CPU at the same time.
- An application can be neither parallel — nor concurrent, which means that it processes all tasks one at a time, sequentially.
- An application can be both parallel — and concurrent, which means that it processes multiple tasks concurrently in multi-core CPU at the same time.
Thread is an independent path of execution.
- Program contains Multiple Process.
- Process is instance of Program in Execution. When the Process starts, it would always start with a Single Thread. From there the No of Threads increases by the Way program has written.
- Threads is instance of Program in Execution.Threads within the process share the same memory as the process. A thread is a basic unit of CPU utilization, consisting of a program counter, a stack, and a set of registers. A thread of execution results from a fork of a computer program into two or more concurrently running tasks.
- Task is a set of program instructions that are loaded in memory. The Piece of runnable code which is loaded or Set of instruction processed by Memory is Task. A “Task” is a piece of work that will execute, and complete at some point in the future.
Two process runs on different memory space unless forked, but all threads share same memory space.
Suppose you are running a Resturant. You have four Orders and Four Chef. A Order is a thread, a Chef is a processor, and a Cooking is a task. The problem you face is how to efficiently schedule the Chef and Orders so that the tasks get done as quickly as possible.
A Task means an action or work you want to do. A Thread may be one of the doer or worker performing that work.
Inter-thread communication (sharing data etc.) is significantly simpler to program than inter-process communication.
Context switches between threads are faster than between processes. That is, it’s quicker for the OS to stop one thread and start running another than do the same with two processes.
Example:
Applications with GUIs typically use one thread for the GUI and others for background computation. The spellchecker in MS Office, for example, is a separate thread from the one running the Office user interface. In such applications, using multiple processes instead would result in slower performance and code that’s tough to write and maintain.
It entirely depends on the design perspective whether to go for a thread or process. When I want to set of logically co-related operations to be carried out parallel. For example, if you run a Notepad++ there will be one thread running in the foreground as an editor and other thread running in background auto saving the document at regular intervals so no one would design a process to do that autosaving task separately.
synchronous – When you execute something synchronously, you wait for it to finish before moving on to another task. You are in a queue to get a movie ticket. You cannot get one until everybody in front of you gets one, and the same applies to the people queued behind you.
asynchronous -When you execute something asynchronously, you can move on to another task before it finishes. i.e. You are in a restaurant with many other people. You order your food. Other people can also order their food, they don’t have to wait for your food to be cooked and served to you before they can order. In the kitchen, restaurant workers are continuously cooking, serving, and taking orders. People will get their food served as soon as it is cooked.
Synchronous (one thread):
Single Thread |--------A--------||--------B--------|
Synchronous (Multi-Threaded):
Thread A |--------A--------|
Thread B |--------B--------|
Thread C |--------C--------|
ASynchronous (One thread):
A-Start ------------------------------------------ A-End
| B-Start -----------------------------------------|--- B-End
| | C-Start ------------------- C-End | |
| | | | | |
V V V V V V
Single thread->|--A-|---B---|--C-|-A-|-C-|--A--|-B-|--C---|---A---|--B-->|
Asynchronous (Multi-Threaded):
Thread A -> |----A-----|
Thread B -----> |-----B-----------|
Thread C ---------> |-------C----------|
A Callable needs to implement call() method while a Runnable needs to implement run() method. A Callable can return a value and throw checked exception. Runnable interface for fire and forget calls, especially when you are not interested in result of the task execution. A Callable can be used with ExecutorService#invokeXXX(Collection> tasks) methods but a Runnable cannot be. Refer here
One important difference: the run() method in the Runnable interface returns void; the call() method in the Callable interface returns an object of type T. This allows you to access a response object easily.
public interface Runnable {
void run();
}
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
It manages a pool of worker threads, and allows you to submit tasks for execution. ExecutorService abstracts away many of the complexities associated with the lower-level abstractions like raw Thread. It provides mechanisms for safely starting, closing down, submitting, executing, and blocking on the successful or abrupt termination of tasks (expressed as Runnable or Callable). ExecutorService handles creation, management, and reusability of threads, making it easier to handle concurrent tasks in multithreaded applications. Refer here
An ExecutorService is a utility in Java that provides a way to execute tasks concurrently and hides the complexities of underlying thread.
Below are some benefits:
- Executor service manage thread in asynchronous way
- Use Future to get the return result after thread completion.
- Manage allocation of work to free thread and resale completed work from thread for assigning new work automatically
- fork – join framework for parallel processing
- Better communication between threads
- invokeAll and invokeAny give more control to run any or all thread at once
- shutdown provide capability for completion of all thread assigned work
- Scheduled Executor Services provide methods for producing repeating invocations of runnables and callables Hope it will help you
The Future interface represents the result of an asynchronous computation.It provides methods to check if the computation is complete, wait for the result, and retrieve the result
execute: Use it for fire and forget calls
submit: Method submit extends base method Executor.execute(Runnable) by creating and returning a Future that can be used to cancel execution and/or wait for completion. In nutshell submit is wrapper around execute
void execute(Runnable command) : Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling thread, at the discretion of the Executor implementation.
submit could take both Runnable and Callable as argument
submit(Callable task) : Submits a value-returning task for execution and returns a Future representing the pending results of the task.
Future submit(Runnable task) : Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future representing that task.
submit() is wrapper around execute and hides exception in the framework itself unless you embed your task code in try{} catch{} block.
execute() throws output when Runnable code actually throws exeception
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService objExecService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
objExecService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 5/0;
System.out.println("Division by zero successful");
}
});
objExecService.shutdown();
}
}
Output
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Main$1.run(Main.java:13)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1130)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:630)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:832)
submit() throws output when Runnable code actually throws exeception
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService objExecService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
objExecService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 5/0;
System.out.println("Division by zero successful");
}
});
objExecService.shutdown();
}
}
Output
Refer here
Thread objects use a significant amount of memory, and in a large-scale application, allocating and deallocating many thread objects creates a significant memory management overhead.Thread pool is a pool of already created worker thread ready to do the job. It creates Thread and manage them. Instead of creating Thread and discarding them once task is done, thread-pool reuses threads in form of worker thread.
Because creation of Thread is time consuming process and it delays request processing.
Threadpool addresses below issues.
- Run time latency for thread creation
- Uncontrolled use of System Resources
It provides a way to separate the task execution logic from the application code, allowing developers to focus on business logic rather than thread management.
The Executor framework consists of two main components:
- Executor interface and the ExecutorService interface. The Executor interface defines a single method, execute(Runnable), which is used to submit tasks for execution.
- The ExecutorService interface extends the Executor interface and provides additional methods for managing the execution of tasks, such as the ability to submit callables and the ability to shut down the executor.
Executor framework also provides a static utility class called Executors ( similar to Collections) which provides several static factory method to create various type of Thread Pool implementation in Java e.g. fixed size thread pool, cached thread pool and scheduled thread pool.best way to get an executor is to use one of the static factory methods provided by the Executors utility class. Some of the available factory methods in Executors class are:
- static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() : Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but will reuse previously constructed threads when they are available.
- static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int numThreads) : Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads.
- static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int numThreads) : Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a given delay, or to execute periodically.
- newSingleThreadExecutor() : Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread.
Executor framework is used for creating threadpool
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
shutdown() method does one thing: prevents clients to send more work to the executor service. This means all the existing tasks will still run to completion unless other actions are taken. This is true even for scheduled tasks, e.g., for a ScheduledExecutorService: new instances of the scheduled task won’t run. It also frees up any background thread resources.
shutdown() method provides graceful application shutdown Prevent your application to submit new tasks, and wait for all the existing tasks to complete before shutting down the JVM.
shutdown() – Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted.
shutdownNow() – Attempts to stop all actively executing tasks, halts the processing of waiting tasks, and returns a list of the tasks that were awaiting execution.
Fork-Join Pools allow you to break down a larger task into smaller subtasks that can be executed concurrently. This is particularly valuable for tasks that can be divided into independent parts, such as recursive algorithms, matrix multiplication, sorting, and searching.This framework is well-suited for tasks that follow a recursive structure. A task is divided into smaller tasks until it reaches the base case, at which point the results are computed.Fork-Join Pools employ work-stealing algorithms, enabling idle threads to ‘steal’ tasks from other threads’ task queues when they have completed their own work.
The Reactor pattern efficiently handles multiple concurrent service requests by dispatching them to appropriate event handlers using a single or a limited number of threads.The idea is that you create a lot of threads which don’t do anything at first. Instead, they “wait for work”. When work arrives (in the form of code), some kind of executor service (the reactor) identifies idle threads from the pool and assigns them work to do.Use when low-latency and high-throughput in server-side applications, making it an essential strategy for modern networking frameworks and web servers
If you have code that performs some long-time operations and only then returns the result Future is used. Future is a placeholder. It doesn’t contain any value as long as the new thread hasn’t finished its work.
Future<String> objFuture = objExecService.submit(() ->{
Thread.sleep(3000);
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
});
System.out.println(objFuture.get());
While the separate thread is calculating something, the main thread continues its work. And when you think it’s finally time the value has got calculated, you write future.get() and get the actual value. But be careful: this time if the value hasn’t yet been assigned and the future is still empty, the main thread will have to wait until it happens
The idea is that you create a lot of threads which don’t do anything at first. Instead, they “wait for work”. When work arrives (in the form of code), some kind of executor service (the reactor) identifies idle threads from the pool and assigns them work to do. Worker Thread makes sense when taking in terms of the reactor pattern, different types of events are run by the handler threads which is similar. A thread is not tied to a single event class but will run any number of different events as they occur.
Interprocess communication (IPC) is a set of programming interfaces that allow a programmer to coordinate activities among different program processes that can run concurrently in an operating system. This allows a program to handle many user requests at the same time. Since even a single user request may result in multiple processes running in the operating system on the user’s behalf, the processes need to communicate with each other. The IPC interfaces make this possible. Each IPC method has its own advantages and limitations so it is not unusual for a single program to use all of the IPC methods.
Java interprocess communication is based at the lowest level on turning state, requests, etc into sequences of bytes that can be sent as messages or as a stream to another Java process. You can do this work yourself, or you can use a variety of “middleware” technologies of various levels of complexity to abstract away the implementation details. Technologies that may be used include, Java object serialization, XML, JSON, RMI, CORBA, SOAP / “web services”, message queing, and so on.
The fundamental difference is that threads live in the same address spaces, but processes live in the different address spaces. This means that inter-thread communication is about passing references to objects and changing shared objects, but processes is about passing serialized copies of objects.In practice, Java interthread communication can be implemented as plain Java method calls on a shared object with appropriate synchronization thrown in.
Inter-Thread Communication = threads inside the same JVM talking to each other.Threads inside the same JVM can use pipelining through lock-free queues to talk to each other with nanosecond latency.
Inter-Process Communication (IPC) = threads inside the same machine but running in different JVMs talking to each other.Threads in different JVMs can use off-heap shared memory (usually acquired through the same memory-mapped file) to talk to each other with nanosecond latency.
Starvation describes a situation where a thread is unable to gain regular access to shared resources and is unable to make progress. This happens when shared resources are made unavailable for long periods by “greedy” threads. For example, suppose an object provides a synchronized method that often takes a long time to return. If one thread invokes this method frequently, other threads that also need frequent synchronized access to the same object will often be blocked.
A thread often acts in response to the action of another thread. If the other thread’s action is also a response to the action of another thread, then livelock may result. As with deadlock, livelocked threads are unable to make further progress. However, the threads are not blocked — they are simply too busy responding to each other to resume work. This is comparable to two people attempting to pass each other in a corridor: Alphonse moves to his left to let Gaston pass, while Gaston moves to his right to let Alphonse pass. Seeing that they are still blocking each other, Alphone moves to his right, while Gaston moves to his left. They’re still blocking each other, so…
Scheduling is order of executuion of threads. JVM would simply use the underlying threading mechanism provided by the OS.
Non-preemptive Scheduling: The current process releases the CPU either by terminating or by switching to the waiting state. (Used in MS Windows family)
Advantages are Decreases turnaround time and Does not require special HW (e.g., timer)
Disadvantages are Limited choice of scheduling algorithm
Preemptive Scheduling: The current process needs to involuntarily release the CPU when a more important process is inserted into the ready queue or once an allocated CPU time has elapsed. (Used in Unix and Unix-like systems).This is determined by priority assigned to thread.Despite priority JVM may decide to execute thread of lower priority inorder to avoid starvation.
Advantages are No limitation on the choice of scheduling algorithm
Disadvantages are Additional overheads (e.g., more frequent context switching, HW timer, coordinated access to data, etc.)
How do you implement Thread in Java?
By extending java.lang.Thread class
By implementing java.lang.Runnable interface.
Which way of implementing Thread is better? Extending Thread class or implementing Runnable method?
Implementing Runnable is better because in Java we can only extend one class so if we extend Thread class we can not extend any other class while by implementing Runnable interface we still have that option open with us
What is the difference between start() and run() method of Thread class?
start() method is used to start newly created thread, while start() internally calls run() method
When you invoke run() as normal method, its called in the same thread, no new thread is started