Everything about pH – Acidic or Alkaline
- pH is the measure of acidity or alkalinity of soil.pH varies between 1 to 14. 1 being most acidic and 14 being most alkaline. 6.5 to 7 is considered as neutral
- pH varies between 1 to 14. 1 being most acidic and 14 being most alkaline. 6.5 to 7 is considered as neutral
- Plants extract iron from the soil by roots. If the soil is alkaline irons bound to the soil.Depending on soil pH mineral bound to soil particle or make it soluble for uptake by plant
- Hydrogen ions are found at very low level. 0.0000001 Molar which is (log10 -7) pH7.pH is concentration of hydrogen ions. The more hydrogen ions are loosely available the lower the pH. The soil would be more acidic not alkaline.
Low the soil pH
Soil that is too acid (having a low Ph between 1.0 and 6.0) will show the following symptoms caused by increased availability of aluminum and a
decreased availability of phosphorus
- wilting leaves
- stunted growth of plant and/or root
- yellow spots on the leaves that turn brown and lead to leaf death
- blighted leaf tips
- poor stem development
High the soil pH
Soil that is too alkaline (having a high Ph between 8.0 and 14.0) will show the following symptoms caused by the plants inability to absorb iron. Phosphorus is
also not readily available and the micronutrients zinc, copper and manganese are also in limited supply.
- Interveinal chlorosis- (light green or yellowing of the leaf with green veining)
- General leaf discoloration
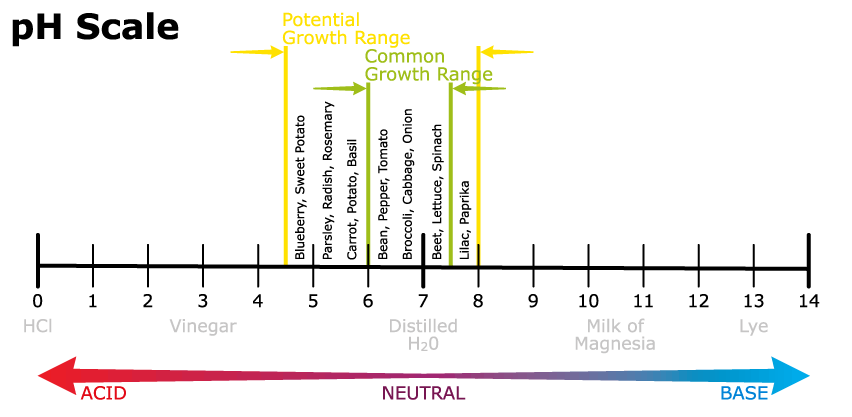
From the ph scale below, certain plants thrive in slightly acidic or slightly alkaline conditions. If you see your asparagus, cauliflower, lettuce, parsley
and spinach thriving you may have more alkaline conditions if your plants like radishes, sweet potatoes, peppers, and carrots are
struggling since they thrive in more acidic conditions and vice versa.