application-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="mugil.org.*" />
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
</bean>
<bean id="entityManagerFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"
p:dataSource-ref="dataSource" p:persistenceUnitName="simple-jpa">
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MUSIC_STORE"/>
<property name="username" value="music_store"/>
<property name="password" value="music_store"/>
</bean>
</beans>
Dissection of application-context.xml
<context:component-scan base-package="mugil.org.*" />
- This component-scan tag also enables the usage of JPA annotations.
- Enables the usage of JPA annotations(@Service, @Component, @Repository, @Controller and etc.,)
- annotation-config —> enables the usage of JPA annotations , only in the beans specified in the context.xml whereas (ii) component-scan —> scans through all the packages specified, records all the project beans having JPA annotations, into this context.xml. Therefore it enables JPA annotaion usage in (beans specified in context.xml)+(Project Beans).Inshort, component-scan extends annotation-config.
Note:
When we use component-scan in the app-context.xml, it’s not necessary to use annotation-config again.Even if both the tags are specified, it’s not a problem because, the spring container would take care of running the process only once.
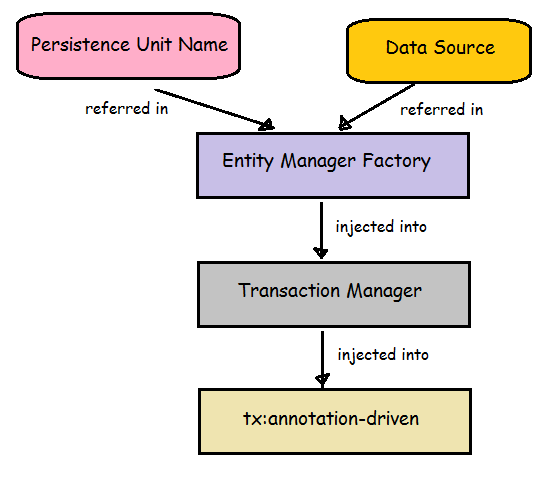
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
- It checks for @Transactional annotation in any of the classes. This tag is like a Transactional Switch that turns on the transactional behaviour.Here Transaction Manager is being injected
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MUSIC_STORE"/>
<property name="username" value="music_store"/>
<property name="password" value="music_store"/>
</bean>
- Here Transaction Manager is setup.EntityManagerFactory is being injected.
- Here EntityManagerFactory is setup .Data Source reference and Persistence UnitName Reference is specified.
- DB connection details are specified.
- Based on the PersistenceUnit name, the corresponding portion of persistence.xml is accessed (a Project can have multiple persistenceUnitNames)
persistence-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name="simple-jpa" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<provider>org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence</provider>
<class>mugil.pojo.MusicDetails</class>
<exclude-unlisted-classes>true</exclude-unlisted-classes>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.dialect" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect"/>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true"/>
<property name="hibernate.max_fetch_depth" value="3"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
Dissection of persistence-context.xml
- persistence-unit – Defines the Name of the Persistence Unit
- provider – ORM tool by which the underlying persistence would be accessed
- class – Entity Class Names
- properties – Defining the underlying persistence technology and other properties would be configured here
Other Java Codes
DaoInterface.java
public interface IMusicStoreDao
{
public List getMusicList();
}
DaoImplementation.java
@Service(value = "MusicCollections")
@Repository(value = "MusicCollections")
@Transactional
public class MusicStoreDaoImpl implements IMusicStoreDao{
@PersistenceContext(unitName = "simple-jpa")
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public List getMusicList(){
List musicDetailsList= entityManager.createQuery("select c from MusicDetails c").getResultList();
return musicDetailsList;
}
}
Executer.java
public class Executer {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("META-INF/app-context.xml");
IMusicStoreDao musicStoreDao=(IMusicStoreDao) applicationContext.getBean("MusicCollections");
System.out.println("MusicList: \n"+musicStoreDao.getMusicList());
}
}
Reference:
Spring and JPA