- Spring sits between the application classes and the O/R mapping tool, undertakes transactions, and manages connection objects.It translates the underlying persistence exceptions thrown by Hibernate to meaningful, unchecked exceptions of type DataAccessException. Moreover, Spring provides IoC and AOP, which can be used in the persistence layer
- Hibernate uses Template Pattern – To clean the code and provide more manageable code, Spring utilizes a pattern called Template Pattern. By this pattern, a template object wraps all of the boilerplate repetitive code. Then, this object delegates the persistence calls as a part of functionality in the template. In the Hibernate case, HibernateTemplate extracts all of the boilerplate code, such as obtaining a Session, performing transaction, and handing exceptions.
- With Spring, the HibernateTemplate object interacts with Hibernate. This object removes the boilerplate code from DAO implementations.Any invocation of one of HibernateTemplate’s methods throws the generic DataAccessException exception instead of HibernateException (a Hibernate-specific exception).Spring lets us demarcate transactions declaratively, instead of implementing duplicated transaction-management code.
- The HibernateTemplate class uses a SessionFactory instance internally to obtain Session objects for Hibernate interaction. Interestingly, you can configure the SessionFactory object via the Spring IoC container to be instantiated and injected into DAO objects.
- Spring provides its own exception hierarchy, which sits on the exception hierarchies of the O/R mapping tools.The Spring exception hierarchy is defined as a subclass of org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException. Spring catches any exception thrown in the underlying persistence technology and wraps it in a DataAccessException instance.The DataAccessException object is an unchecked exception, because it extends RuntimeException and you do not need to catch it if you do not want to.
- Spring provides distinct DAO base classes for the different data-access technologies it supports. When you use Hibernate with Spring, the DAO classes extend the Spring org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport class. This class wraps an instance of org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate, which in turn wraps an org.hibernate.SessionFactory instance.
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport | org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate | org.hibernate.SessionFactory - HibernateException is thrown for any failure when directly interacting with Hibernate. When Spring is used, HibernateException is caught by Spring and translated to DataAccessException for any persistence failure. Both exceptions are unchecked, so you do not need to catch them if you don’t want to do.
-
DAO Implementation using DAOSupport
StudentDao.javaimport java.util.Collection; public interface StudentDao { public Student getStudent(long id); public Collection getAllStudents(); public Collection findStudents(String lastName); public void saveStudent(Student std); public void removeStudent(Student std); }Using DAOSupport Object
StudentDao.javaimport org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport; import java.util.Collection; public class HibernateStudentDao extends HibernateDaoSupport implements StudentDao { public Student getStudent(long id) { return (Student) getHibernateTemplate().get(Student.class, new Long(id)); } public Collection getAllStudents() { return getHibernateTemplate().find("from Student std order by std.lastName, std.firstName"); } public Collection findStudents(String lastName) { return getHibernateTemplate().find("from Student std where std.lastName like ?", lastName + "%"); } public void saveStudent(Student std) { getHibernateTemplate().saveOrUpdate(std); } public void removeStudent(Student std) { getHibernateTemplate().delete(std); } } - all of the persistent methods in the DAO class use the getHibernateTemplate() method to access the HibernateTemplate object.
- HibernateTemplate is a Spring convenience class that delegates DAO calls to the Hibernate Session API. This class exposes all of Hibernate’s Session methods, as well as a variety of other convenient methods that DAO classes may need. Because HibernateTemplate convenient methods are not exposed by the Session interface, you can use find() and findByCriteria() when you want to execute HQL or create a Criteria object.
- Using the HibernateDaoSupport class as the base class for all Hibernate DAO implementations would be more convenient, but you can ignore this class and work directly with a HibernateTemplate instance in DAO classes. To do so, define a property of HibernateTemplate in the DAO class, which is initialized and set up via the Spring IoC container.
-
DAO Implementation Using HibernateTemplate
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate; import java.util.Collection; public class HibernateStudentDao implements StudentDao { HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate; public Student getStudent(long id) { return (Student) getHibernateTemplate().get(Student.class, new Long(id)); } public Collection getAllStudents() { return getHibernateTemplate().find("from Student std order by std.lastName, std.firstName"); } public Collection findStudents(String lastName) { return getHibernateTemplate().find("from Student std where std.lastName like "+ lastName + "%"); } public void saveStudent(Student std) { getHibernateTemplate().saveOrUpdate(std); } public void removeStudent(Student std) { getHibernateTemplate().delete(std); } public HibernateTemplate getHibernateTemplate() { return hibernateTemplate; } public void setHibernateTemplate(HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate) { this.hibernateTemplate = hibernateTemplate; } } - The DAO class now has the setHibernateTemplate() method to allow Spring to inject the configured HibernateTemplate instance into the DAO object.Moreover, the DAO class can abandon the HibernateTemplate class and use the SessionFactory instance directly to interact with Hibernate.
Using SessionFactory Object
import org.hibernate.HibernateException; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Query; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.SessionFactoryUtils; import java.util.Collection; public class HibernateStudentDao implements StudentDao { SessionFactory sessionFactory; public Student getStudent(long id) { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { return (Student) session.get(Student.class, new Long(id)); } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public Collection getAllStudents() { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { Query query = session.createQuery("from Student std order by std.lastName, std.firstName"); Collection allStudents = query.list(); return allStudents; } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public Collection getGraduatedStudents() { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { Query query = session.createQuery("from Student std where std.status=1"); Collection graduatedStudents = query.list(); return graduatedStudents; } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public Collection findStudents(String lastName) { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { Query query = session.createQuery("from Student std where std.lastName like ?"); query.setString(1, lastName + "%"); Collection students = query.list(); return students; } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public void saveStudent(Student std) { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { session.save(std); } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public void removeStudent(Student std) { Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.getSession(this.sessionFactory, true); try { session.delete(std); } catch (HibernateException ex) { throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex); } finally { SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session); } } public void setSessionFactory(SessionFactory sessionFactory) { this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory; } } - In all of the methods above, the SessionFactoryUtils class is used to obtain a Session object. The provided Session object is then used to perform the persistence operation. SessionFactoryUtils is also used to translate HibernateException to DataAccessException in the catch blocks and close the Session objects in the final blocks. Note that this DAO implementation bypasses the advantages of HibernateDaoSupport and HibernateTemplate. You must manage Hibernate’s Session manually (as well as exception translation and transaction management) and implement much boilerplate code.
- org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.SessionFactoryUtils is a Spring helper class for obtaining Session, reusing Session within transactions, and translating HibernateException to the generic DataAccessException.
- In cases where you need to work directly with Session objects, you can use an implementation of the org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateCallback interface as the handler to work with Sessions.
-
An implicit implementation of HibernateCallback is created and its only doInHibernate() method is implemented. The doInHibernate() method takes an object of Session and returns the result of persistence operation, null if none. The HibernateCallback object is then passed to the execute() method of HibernateTemplate to be executed. The doInHibernate() method just provides a handler to work directly with Session objects that are obtained and used behind the scenes.
Using HibernateCallback
public void saveStudent(Student std) { HibernateCallback callback = new HibernateCallback() { public Object doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException, SQLException { return session.saveOrUpdate(std); } }; getHibernateTemplate().execute(callback); }
Daily Archives: November 9, 2017
Data Access Object Design Pattern
In a Application the persistence unit used to store the data may vary.Accessing data varies depending on the source of the data. Access to persistent data varies greatly depending on the type of storage (database, flat files, xml files, and so on) and it even differs from its implementation (for example different SQL-dialects).
The advantage of the DAO layer is that if you need to change the underlying persistence mechanism you only have to change the DAO layer, and not all the places in the domain logic where the DAO layer is used from. The DAO layer usually consists of a smaller set of classes, than the number of domain logic classes that uses it.
Abstract and encapsulate all access to the data and provide an interface. This is called the Data Access Object pattern. In a nutshell, the DAO “knows” which data source (that could be a database, a flat file or even a WebService) to connect to and is specific for this data source (e.g. a OracleDAO might use oracle-specific data types, a WebServiceDAO might parse the incoming and outgoing message etc.)
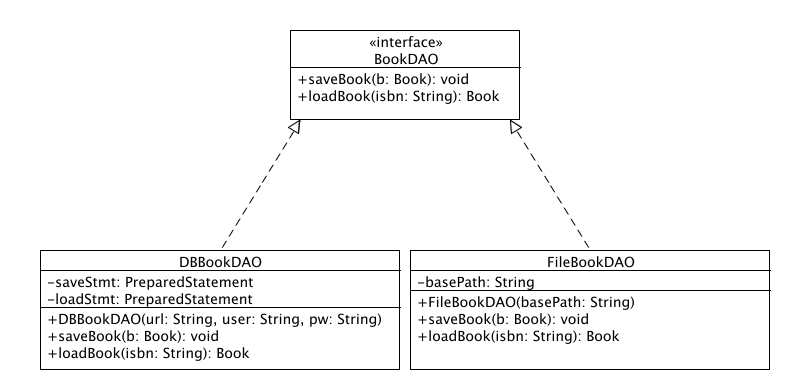
BookDAO.java
public interface BookDAO {
public void saveBook(Book b);
public Book loadBook(String isbn);
}
DBBookDAO.java
public class DBBookDAO implements BookDAO {
private PreparedStatement saveStmt;
private PreparedStatement loadStmt;
public DBBookDAO(String url, String user, String pw) {
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw);
saveStmt = con.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO books(isbn, title, author) "
+"VALUES (?, ?, ?)");
loadStmt = con.prepareStatement("SELECT isbn, title, author FROM books "
+"WHERE isbn = ?");
}
public Book loadBook(String isbn) {
Book b = new Book();
loadStmt.setString(1, isbn);
ResultSet result = loadStmt.executeQuery();
if (!result.next()) return null;
b.setIsbn(result.getString("isbn"));
b.setTitle(result.getString("title"));
b.setAuthor(result.getString("author"));
return b;
}
public void saveBook(Book b) {
saveStmt.setString(1, b.getIsbn());
saveStmt.setString(2, b.getTitle());
saveStmt.setString(3, b.getAuthor());
saveStmt.executeUpdate();
}
}
FileBookDAO.java
public class FileBookDAO implements BookDAO {
private String basePath;
public FileBookDAO(String basePath) {
this.basePath = basePath;
}
public Book loadBook(String isbn) {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(basePath + isbn);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
Book b = new Book();
String rIsbn = br.readLine();
String rTitle = br.readLine();
String rAuthor = br.readLine();
if (rIsbn.startsWith("ISBN: ")) {
b.setIsbn(rIsbn.substring("ISBN: ".length()));
} else {
return null;
}
if (rTitle.startsWith("TITLE: ")) {
b.setTitle(rTitle.substring("TITLE: ".length()));
} else {
return null;
}
if (rAuthor.startsWith("AUTHOR: ")) {
b.setAuthor(rAuthor.substring("AUTHOR: ".length()));
} else {
return null;
}
return b;
}
public void saveBook(Book b) {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(basePath + b.getIsbn() + ".book");
fw.write("ISBN: " + b.getIsbn());
fw.write("TITLE: " + b.getTitle());
fw.write("AUTHOR: " + b.getAuthor());
fw.close();
}
}
Template Pattern
What is Template Pattern?
Template pattern, an abstract class exposes a ways to execute its methods. The subclasses can override the method implementation as per need but the invocation is to be in the same way as defined by an abstract class
When to use Template Pattern?
- When behaviour of an algorithm can vary, you let subclasses implement the behaviour through overriding
- You want to avoid code duplication, implementing variations of the algorithm in subclasses
- You want to control the point that subclassing is allowed.